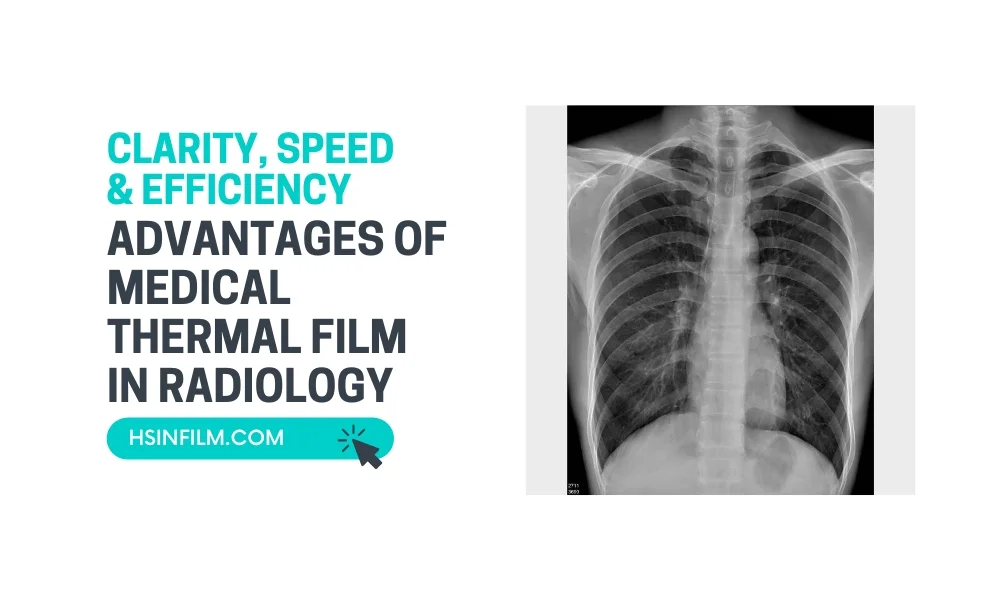
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. One of the most reliable and efficient tools for producing high-quality diagnostic images is medical thermal film. This specialized film, used in conjunction with medical thermal printers, offers several advantages over traditional methods like wet processing or laser imaging.
In this article, we will explore the key benefits of medical thermal film in radiology, emphasizing why it has become a preferred choice for healthcare facilities worldwide.
Table of Contents
What is Medical Thermal Film?
Ever been intrigued by the name? Medical Thermal Film. It sounds like something straight out of a sci-fi movie. In layman’s terms, it’s a film sensitive to temperature changes, capturing images when exposed to heat. More than just a product, it’s a technological marvel designed to ensure impeccable image quality, especially in the delicate field of medical imaging.
Historical Context: Imaging Before Thermal Film
Remember those times when getting an X-ray meant waiting anxiously while your film was being developed in some mysterious darkroom? Traditional imaging methods, although revolutionary in their times, had their fair share of challenges:
- Longer waiting times.
- Possibility of images getting over or under-exposed.
- The recurrent issue of image blurring.
Enter the advantages of medical thermal film, and the game is forever changed.
Factors Affecting Image Quality in Medical Thermal Film
Medical thermal film plays a critical role in diagnostic imaging, offering a physical record of X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. However, achieving high-quality images depends on several key factors. Let’s break down the essentials:
1. Resolution – The Sharpness of the Image
Resolution refers to how detailed an image appears. Higher resolution means finer details and clearer images.
- Importance: In medical imaging, high resolution helps detect subtle abnormalities, ensuring accurate diagnosis.
- Factors Affecting Resolution:
- Printer DPI (Dots Per Inch): A higher DPI produces sharper images. Most medical thermal printers range between 300 to 600 DPI.
- Thermal Head Condition: A clean, well-maintained thermal head ensures precise printing. Dirt or wear can lead to blurring.
2. Contrast – The Difference Between Light and Dark Areas
Contrast determines how well different tissues or structures stand out in the image.
- Importance: Proper contrast helps highlight fractures, tumors, or dense tissues.
- Factors Affecting Contrast:
- Temperature Settings: Higher heat can enhance darker areas, while lower heat lightens the image.
- Film Sensitivity: Higher-quality thermal film reacts more effectively to temperature changes, enhancing contrast.
3. Gray-Scale Resolution – The Range of Shades Between Black and White
Gray-scale resolution reflects the number of distinct gray levels the film can display.
- Importance: A broader gray scale allows for more nuanced images, which is vital for distinguishing soft tissues.
- Factors Affecting Gray-Scale:
- Printer Capability: Advanced printers offer 256 gray levels or more, providing richer, smoother gradients.
- Film Type: Premium thermal films can capture finer gray-scale details, improving diagnostic accuracy.
4. Environmental Factors
External factors can also influence image quality.
- Temperature and Humidity: Excessive heat or moisture can degrade thermal film, leading to faded or distorted images.
- Storage Conditions: Properly storing thermal film in a cool, dry place helps maintain its quality over time.
5. Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration of thermal printers ensures consistent image quality. Routine maintenance prevents issues like uneven heating or poor gray-scale representation.
By focusing on these factors, healthcare professionals can produce clearer, more reliable images for accurate diagnosis.
Advantages of Medical Thermal Film
1. High Image Quality and Precision
Medical thermal film is known for delivering sharp, high-resolution images that are essential for accurate diagnoses. The thermal printing process ensures that even the smallest anatomical details are captured with clarity, allowing radiologists to detect abnormalities with confidence.
- Consistency in Quality: Unlike wet processing, thermal imaging eliminates variability, producing uniform results every time.
- Grayscale Accuracy: The precise grayscale reproduction enhances the visibility of fine structures in X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
2. Dry Processing – No Chemicals Required
One of the biggest advantages of thermal film is that it does not require chemical processing. Traditional radiology films often involve complex and hazardous chemical baths, but thermal film uses heat to develop images.
- Eco-Friendly: Eliminates the need for chemical disposal, reducing the environmental impact.
- Cost-Effective: No need to purchase and maintain chemical processing equipment.
- Simplified Workflow: Faster processing without waiting for film development.
3. Faster Image Production
Time is critical in medical diagnostics. Thermal printers produce high-quality images in seconds, making them ideal for busy radiology departments.
- Rapid Turnaround: Instant image development speeds up the diagnosis and treatment process.
- Emergency Ready: Essential for urgent cases where quick imaging is required.
4. Durability and Longevity
Medical thermal film is highly durable and resistant to environmental factors like humidity, light, and handling. This durability ensures that images remain intact and legible for extended periods.
- Long Shelf Life: Can be stored for years without degradation.
- Archival Quality: Perfect for maintaining long-term medical records.
5. Cost Efficiency
Switching to medical thermal film can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Lower Operational Costs: Eliminates the need for chemicals, darkrooms, and complex maintenance.
- Reduced Waste: Less material waste compared to traditional films.
- Minimal Training Required: Easy to operate, reducing staff training costs.
6. Space-Saving Design
Thermal printers used for developing medical thermal film are typically compact and lightweight. This allows healthcare facilities to save valuable space.
- Small Footprint: Can be installed in smaller imaging rooms without sacrificing quality.
- Portable Options: Some thermal printers are portable, allowing for use in mobile radiology units.
7. Enhanced Patient Care
Faster image production and high-quality results translate to better patient care. Radiologists can make quicker, more accurate diagnoses, leading to faster treatment plans and improved patient outcomes.
- Reduced Wait Times: Patients receive results faster, reducing anxiety and expediting treatment.
- Improved Diagnostic Confidence: Clearer images help detect conditions at earlier stages.
8. Compatibility with Digital Imaging
Medical thermal film can seamlessly integrate with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and other digital imaging platforms. This allows for easy conversion of digital images into high-resolution hard copies.
- Flexible Use: Supports digital workflows while maintaining the option for physical film.
- Consistent with DICOM Standards: Ensures compatibility across different imaging modalities.
9. Reduced Maintenance Requirements
Thermal printers are designed to operate with minimal maintenance, making them highly reliable for continuous use.
- Fewer Breakdowns: Simplified mechanics reduce the risk of malfunctions.
- Lower Downtime: Consistent performance ensures uninterrupted service.
10. Improved Workflow Efficiency
Thermal imaging streamlines radiology workflows by reducing the steps involved in producing and managing films.
- Direct Printing from Imaging Devices: Eliminates manual processing.
- Batch Printing Capabilities: Allows for large volumes of films to be produced quickly.
11. Unparalleled Clarity with Thermal Film
Isn’t clarity what we seek in every image? Especially in a field where a clearer image can literally mean the difference between life and death. The thermal film offers:
- Sharper images: Defined outlines and intricate details become visible.
- Greater contrast: Differentiating between tissues becomes seamless.
- Fewer retakes: A win-win for both the patient and the radiologist.
Imagine diagnosing a hairline fracture without the image clarity that thermal films offer. Unthinkable!
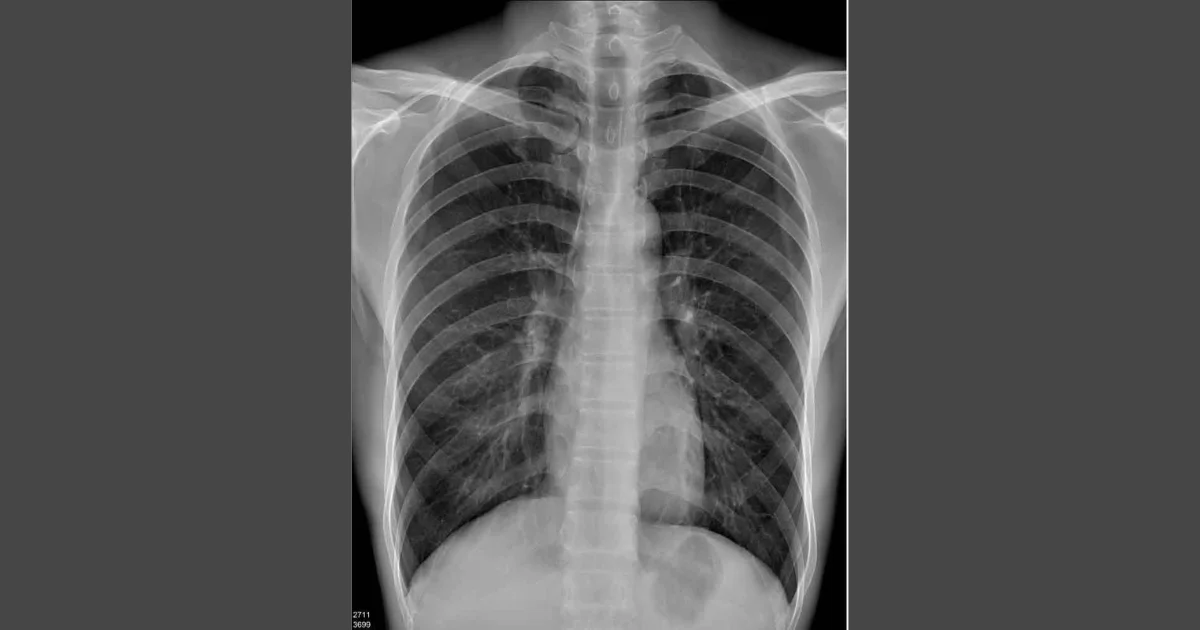
In critical medical scenarios, every second counts. Time spent waiting for a film to develop might equate to golden treatment hours lost. With thermal film:
- Instantaneous results become the norm.
- Swift decisions based on clear images can be made.
- A patient’s wait time? Drastically reduced!
Real-World Applications
- Orthopedics: Producing high-resolution X-rays of bones and joints.
- Dentistry: Printing detailed dental scans.
- Mammography: Capturing clear breast tissue images.
- Cardiology: Printing angiography and echocardiography results.
Challenges and Solutions of Medical Thermal Film
Medical thermal film plays a crucial role in producing hard copies of diagnostic images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Despite its utility, healthcare facilities often encounter challenges that can affect image quality and durability. Let’s explore these challenges and practical solutions to overcome them.
1. Challenge: Limited Resolution
Thermal film has a lower resolution compared to digital and laser imaging technologies. This can lead to less detailed images, making it harder to detect subtle fractures or soft tissue changes.
Solution:
- Use high-resolution thermal printers specifically designed for medical imaging.
- Adjust printer settings to optimize contrast and sharpness for each type of scan.
2. Challenge: Gray-Scale Limitations
Thermal film often lacks the wide gray-scale range required for capturing subtle differences in soft tissues, which is critical for mammography or vascular imaging.
Solution:
- Enhance image pre-processing before printing to maximize the contrast within the available gray-scale range.
- For cases requiring high gray-scale precision, use laser film or digital formats as alternatives.
3. Challenge: Environmental Sensitivity
Thermal film is highly sensitive to heat, humidity, and light. Exposure can degrade image quality, causing fading or distortion over time.
Solution:
- Store thermal film in a cool, dry environment away from direct light sources.
- Implement temperature-controlled storage for long-term archiving.
4. Challenge: Image Longevity
Unlike traditional X-ray film, thermal images may degrade faster, making long-term archiving a challenge.
Solution:
- Digitize important thermal film records for long-term storage.
- Reprint essential films periodically to maintain clear copies for medical records.
5. Challenge: Printer Maintenance
Thermal printers require regular maintenance. Dust, misaligned print heads, and worn-out components can lead to artifacts, smudges, or uneven prints.
Solution:
- Schedule routine maintenance and cleaning for thermal printers.
- Train staff to recognize early signs of printer issues and address them promptly.
6. Challenge: Cost of Consumables
Thermal film and printer components can be costly over time, especially when reprints or replacements are required frequently.
Solution:
- Use high-quality film that provides durability and fewer reprints.
- Consider bulk purchasing or supplier contracts to reduce costs.
7. Challenge: Limited Film Sizes
Thermal film printers may not support all image sizes, leading to difficulties in printing larger diagnostic images.
Solution:
- Utilize tiling or multi-sheet printing for larger images.
- For specialized imaging, use alternative printing technologies like laser imaging.
By applying the right solutions—ranging from equipment maintenance to digital backups—healthcare providers can continue to rely on thermal film as a valuable diagnostic tool.
Conclusion
As we stand at the intersection of technology and healthcare, embracing innovations like medical thermal films seems not just wise but imperative. With unparalleled clarity, efficiency, and a plethora of other advantages, isn’t it time we redefine the future of radiological imaging?
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any side effects associated with medical thermal film imaging?
Typically, no. Thermal films are just mediums to capture images. The side effects, if any, would arise from the imaging technique itself, not the film.
How do medical thermal films compare in cost to traditional imaging methods?
The initial setup might be pricier, but the long-term benefits in terms of clarity, efficiency, and reduced chemical usage make it a cost-effective choice.
Are thermal films suitable for all types of radiological imaging?
Predominantly, yes. However, their application might vary based on specific radiology requirements.
References
- What factors affect the long-range-infrared thermal imaging effect?
- Challenges of Thermographic Image in Medical Applications
This article offers an in-depth exploration of the advantages of medical thermal film in radiology. With every medical advancement, we move closer to ensuring a healthier future. And with thermal films, this future seems clearer than ever.