Welcome to the behind-the-scenes of constructing a medical marvel—a state-of-the-art X-ray room. Imagine a space where science meets compassion, where the heartbeat of diagnostics echoes. In this journey, we’ll guide you through the intricacies of how to build an X-ray room that not only complies with regulations but becomes a sanctuary for health and healing.
Table of Contents: How to Build an X-Ray Room
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the Rulebook
Embarking on the journey of building an X-ray room requires a deep dive into the intricate world of regulations. Picture yourself as a navigator, carefully charting the course through local, state, and national rulebooks. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about creating a haven where every detail aligns with the expectations set by the guardians of healthcare standards.
Also read: Chiropractors in Diagnostic Imaging
Consult with Experts: Building Dreams Together
Why embark on this odyssey alone when you can have dreamweavers by your side? Engage with architects and specialists in medical facility design—imagine them as architects of dreams. Collaborate to sculpt a vision that not only meets safety standards but transcends them, creating a space where innovation and care intertwine.
Site Selection: Choosing a Heartbeat Location
Selecting a location for your X-ray room is akin to choosing a heartbeat for your medical facility. Envision a place that beats with accessibility, harmonizes with zoning regulations, and holds the promise of future growth. This isn’t just a physical location; it’s the pulse of your commitment to healthcare excellence.
Room Design: Crafting Spaces for Care and Comfort
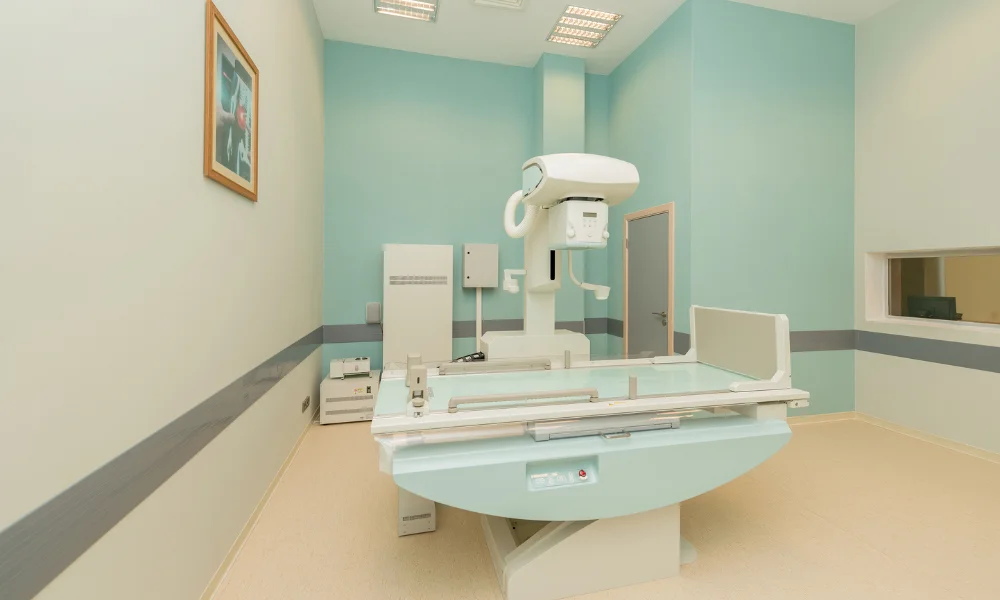
Imagine the X-ray room as a canvas, waiting to be painted with care and comfort. Work closely with architects to design a layout that goes beyond functionality. It’s about creating spaces—a symphony of the X-ray room, control area, waiting room, and facilities like changing rooms and bathrooms. Integrate radiation shielding materials like an artist adding protective layers to a masterpiece.
Equipment Selection: The Heart of the Operation
Choosing an X-ray machine isn’t just a decision; it’s choosing the heartbeat of your diagnostic operation. Picture yourself in a room filled with possibilities. Select the machine that resonates with your intended applications, whether it’s general radiography, fluoroscopy, or mammography. Feel the heartbeat of safety as you prioritize machines with necessary safety features, ensuring compliance dances hand in hand with efficiency.
Structural Considerations: Building on Solid Ground
Imagine your X-ray room as a fortress of healthcare, standing tall on solid ground. Reinforce walls as if fortifying the castle walls, bearing the weight of lead shielding with grace. Visualize the ceiling height not just as an architectural element but as a canvas allowing the X-ray tube to dance freely, ensuring patient positioning is an art, not a compromise.
Electrical Requirements: Powering Up the Possibilities
Collaborate with an electrician as if partnering with a wizard of power. Feel the excitement as you power up the possibilities, meeting every electrical requirement for the X-ray machine, control panel, and accompanying equipment. It’s not just about meeting standards; it’s about creating an electrifying environment where diagnostic magic happens.
Radiation Safety Measures: Shields of Protection
Enter the realm of safety as if donning a superhero cape. Install warning signs that serve as shields, marking radiation areas for all to see. Picture yourself as a guardian, developing and enforcing safety protocols that wrap both staff and patients in a protective embrace. Safety isn’t just a measure; it’s a culture you cultivate.
Lead Apron Storage: Safekeeping Superheroes
Designate a space for your superheroes—lead aprons and radiation protection gear. Feel the responsibility as you create a secure and accessible area. It’s not just storage; it’s safekeeping for those who stand on the frontline of diagnostic care.
Quality Assurance and Compliance: Ensuring Excellence
Imagine your X-ray room as a performer on the grand stage of healthcare. Regular quality assurance tests are not rehearsals; they are performances ensuring your equipment always takes the spotlight. Compliance isn’t a checklist; it’s a commitment to excellence, a promise that your facility will always deliver top-tier diagnostics.
Radiation Monitoring: Eyes on Safety
Picture yourself as a vigilant guardian, eyes fixed on safety. Install devices that act as vigilant sentinels, monitoring radiation levels within and around the X-ray room. It’s not just monitoring; it’s a constant reassurance that safety is a non-negotiable priority.
Final Inspection: Unveiling Perfection
The final inspection is the grand unveiling of your masterpiece. Picture the authorities as appreciative art critics, ensuring every stroke of compliance, every nuance of safety, aligns seamlessly. It’s not just an inspection; it’s the recognition that your facility is a masterpiece worthy of saving lives.
Conclusion: Crafting the Future of Diagnostics
As we bid farewell to this journey of building an X-ray room, remember—it’s not just about bricks and mortar. It’s about crafting a future where health and healing intertwine, where every decision is an emotional investment in saving lives.
FAQs – Answering Your Curiosities
- Can I build an X-ray room without consulting experts?
No, you can’t. Imagine building a dream without architects—it’s like trying to compose a symphony without musicians. Collaborate with experts to ensure your project is a harmonious masterpiece. - How often should I perform quality assurance tests on the X-ray equipment?
Regularly. Think of it like tuning a musical instrument; consistent tests guarantee your equipment produces a symphony of accurate and reliable results. - Do I really need lead-lined walls?
Absolutely. Imagine lead-lined walls as the protective armor of your fortress. They shield both staff and patients from unnecessary radiation exposure, a crucial element in any X-ray room. - What happens during the final inspection?
The final inspection is the grand reveal, akin to lifting the curtain on a theatrical masterpiece. Authorities play the role of appreciative spectators, meticulously examining every detail. It’s not just about meeting regulations; it’s about unveiling a perfect synthesis of safety, precision, and dedication. Picture this moment as the crescendo of your symphony, where each element harmonizes to create a facility worthy of commendation. - Why is radiation monitoring essential?
Think of radiation monitoring as the watchful guardian of your healthcare sanctum. Installing monitoring devices isn’t just a formality; it’s a commitment to vigilant care. It ensures that every heartbeat within the X-ray room is safeguarded, and the surrounding areas remain untouched by any unnecessary exposure. Monitoring is not just a measure; it’s a continuous pledge to keep the healing environment pristine.