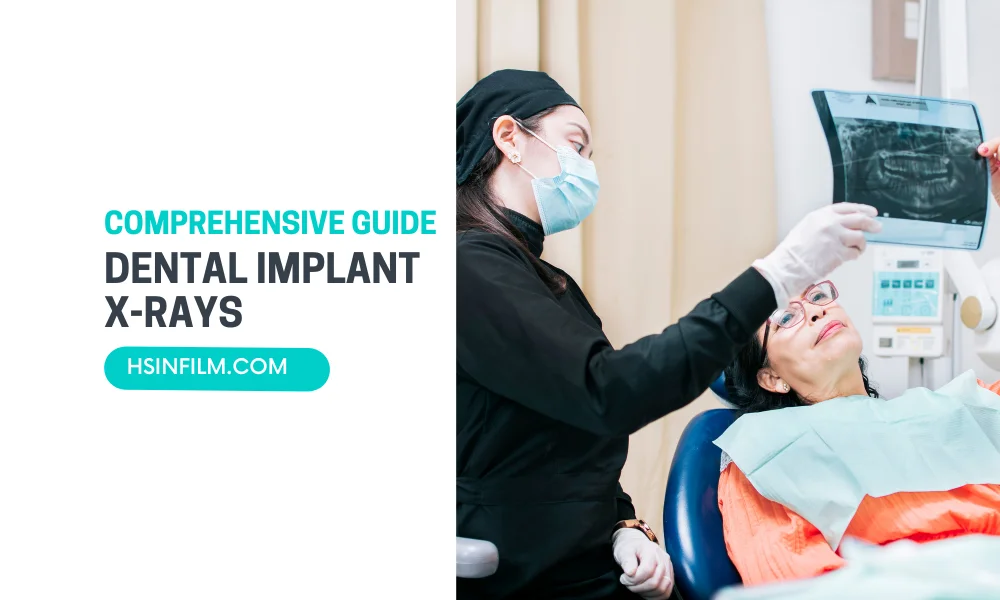
Dental implants stand as a beacon of innovation, offering a transformative solution for replacing missing teeth. At the heart of successful dental implant procedures lies a meticulous planning process, and a cornerstone of this planning is the utilization of dental implant X-rays. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of dental implant X-rays, providing insights into their types, significance, and their pivotal role in achieving seamless and successful treatment outcomes.
Table of Contents
Understanding Dental Implants
Dental implants mark a revolutionary shift in restoring both function and aesthetics in oral health. Unlike traditional solutions, implants mimic natural teeth, offering stability for confident biting and speaking. Meticulously crafted crowns ensure a seamless blend with existing teeth, radiating natural beauty.
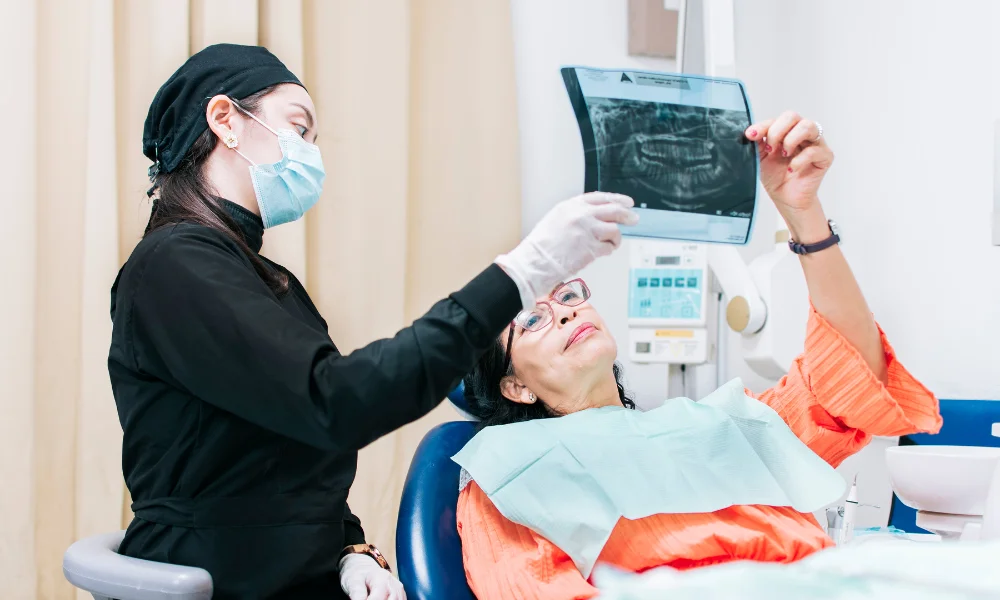
A key feature is osseointegration, allowing implants to integrate with the jawbone, preventing bone loss. Beyond aesthetics, implants contribute to overall oral health by maintaining jaw integrity. This patient-centric approach empowers individuals to regain confidence in smiling, speaking, and eating without limitations.
Dental implants go beyond cosmetic enhancements, embodying a paradigm shift in tooth replacement. They represent not just technological innovation but a transformative solution prioritizing overall well-being in modern dentistry.
Also read: Sprained Ankle X-ray vs Normal Imaging
The Crucial Role of Treatment Planning in Dental Implantology
The significance of meticulous treatment planning extends far beyond aesthetics. In this section, we emphasize the critical importance of thorough and precise treatment planning in ensuring the longevity and success of dental implant procedures.
- Ensuring Longevity:
- Meticulous treatment planning involves a detailed evaluation of the patient’s oral health, considering aspects such as gum condition, bone density, and overall systemic health.
- This comprehensive understanding guides practitioners in making informed decisions about implant size, placement, and type.
- Factors Influencing Success
- Successful dental implant procedures hinge on a combination of factors, each intricately linked to the treatment planning phase.
- Precise measurements, 3D imaging, and a thorough examination of the patient’s medical history contribute to a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Patient-Specific Considerations
- Every patient is unique, and their dental implant treatment should reflect this individuality.
- Treatment planning takes into account specific patient considerations, such as their bite, jaw structure, and overall health.
By emphasizing the importance of thorough assessments and patient-specific considerations, this piece highlights how meticulous planning sets the stage for the overall success and longevity of dental implant procedures.
Exploring the Types of Dental Implant X-Rays
Various types of X-rays play a pivotal role in comprehensive diagnostics. This section delves into three key types of dental implant X-rays, shedding light on their distinct features and applications.
Panoramic X-Rays: A Broad Overview
- Overview:
- Panoramic X-rays provide a comprehensive examination of the entire oral cavity, capturing a broad view of teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures.
- This type of imaging facilitates an overall assessment of oral health, offering a valuable tool for identifying potential issues beyond specific teeth.
- Applications:
- Valuable for initial assessments and treatment planning due to the broad coverage.
- Useful in identifying issues such as impacted teeth, jaw disorders, and overall bone health.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): Precision in Three Dimensions
- Overview:
- CBCT is a sophisticated imaging technique that provides three-dimensional views of dental structures.
- This method involves a cone-shaped X-ray beam, offering detailed anatomical insights crucial for precise treatment planning in dental implant procedures.
- Applications:
- Essential for detailed evaluations of bone density, tooth orientation, and anatomical relationships.
- Particularly valuable for complex cases, enabling practitioners to visualize structures from multiple angles.
Periapical X-Rays: Focused Assessment for Implant Feasibility
- Overview:
- Periapical X-rays focus on specific tooth roots and surrounding structures, offering a detailed view of the targeted area.
- This type of imaging is instrumental in assessing the feasibility of implant placement in specific locations.
- Applications:
- Vital for evaluating the health of tooth roots and adjacent bone structures.
- Used to determine the suitability of a site for dental implant placement, considering factors like bone quality and proximity to vital structures.
Each type of X-ray serves a specific purpose, contributing to the comprehensive assessment and precise planning required for successful dental implant procedures.
Significance of Dental Implant X-Rays in Treatment Planning
X-rays play a pivotal role in shaping effective treatment plans. This section delves into the crucial significance of dental implant X-rays, focusing on pre-operative assessment and the tailoring of treatment plans based on individual patient factors.
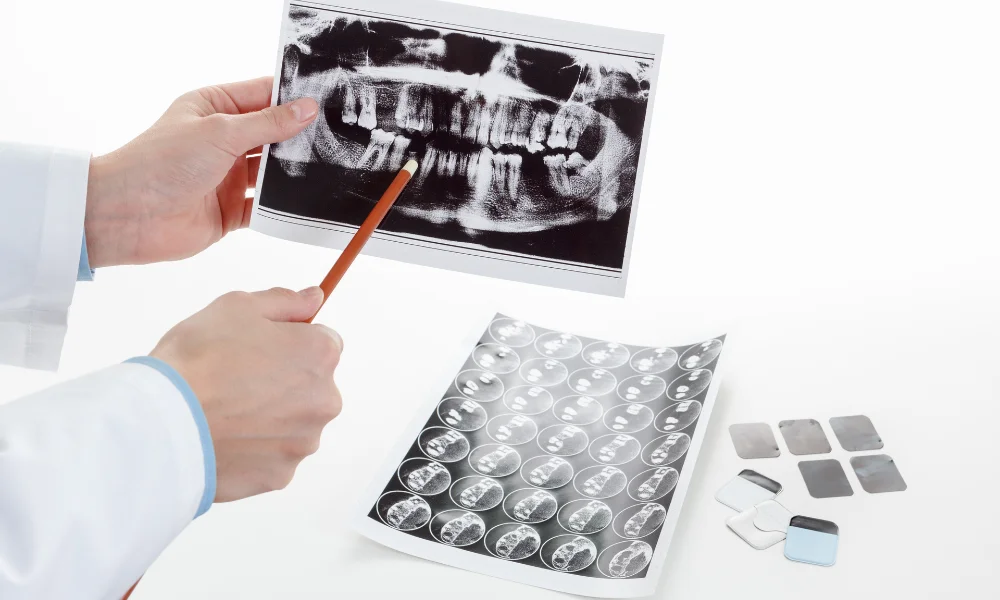
Pre-Operative Assessment: Unveiling the Foundation
- Evaluating Bone Density:
- X-rays provide a detailed view of the patient’s jawbone, allowing practitioners to assess bone density.
- This information is crucial for determining the suitability of the bone for implant placement and understanding the potential need for bone grafting.
- Identifying Anatomical Structures:
- X-rays reveal the intricate details of anatomical structures, including nerves and sinus cavities.
- Accurate identification of these structures is essential to avoid complications during the implant procedure and ensure patient safety.
- Determining Optimal Implant Locations:
- By assessing bone quality and anatomical features, X-rays assist in pinpointing the optimal locations for implant placement.
- This contributes to the precision of the procedure and enhances the chances of successful osseointegration.
Tailoring Treatment Plans: Precision in Personalization
- Customizing Based on Anatomy:
- X-rays provide a personalized view of individual patient anatomy, allowing for treatment plans tailored to specific needs.
- Customization based on X-ray insights ensures that implants are placed in positions that align with the patient’s unique oral structure.
- Addressing Specific Dental Needs:
- Understanding the specifics of a patient’s dental condition is paramount in creating effective treatment plans.
- X-rays aid in identifying issues such as tooth spacing, root health, and the presence of any pathology, guiding practitioners in addressing these concerns.
From the foundational aspects of assessing bone density and identifying anatomical structures to the personalized precision of tailoring treatment plans, X-rays serve as indispensable tools. Their role in ensuring a thorough pre-operative assessment and the customization of treatment plans contributes to the overall success and longevity of dental implant procedures.
Radiographic Guides and Templates in Implant Dentistry
The integration of radiographic guides and templates with X-rays plays a pivotal role in achieving precision in implant placement. This section navigates through the intricacies of this integration, highlighting its significance in ensuring accurate and effective implant procedures.
Navigating Precision: The Essence of Integration
- Understanding Radiographic Guides:
- Radiographic guides are tools that aid in the precise positioning of X-ray imaging.
- These guides provide a framework for capturing images that are crucial for evaluating bone density, assessing anatomical structures, and planning implant placement.
- Templates for Accurate Planning:
- Templates, often created based on radiographic information, assist in planning the exact location and angulation of implants.
- They serve as visual aids, allowing practitioners to foresee the implant’s position in relation to surrounding structures and plan accordingly.
Integration Process: How it Works
- Capturing Comprehensive X-rays:
- Radiographic guides ensure comprehensive X-rays are taken, covering the entire oral anatomy.
- This ensures that practitioners have detailed information about bone density, neighboring teeth, and critical structures.
- Mapping Implant Locations:
- Using the radiographic information, templates are designed to map out the precise locations for implant placement.
- This process considers factors such as bone quality, available space, and proximity to vital structures.
- Enhancing Precision in Placement:
- The integration of radiographic guides and templates enhances precision during the actual implant placement.
- Practitioners can follow the pre-determined plan, minimizing the margin of error and optimizing the chances of successful implant integration.
Benefits of Integration: Precision and Predictability
- Reduced Complications:
- Precise planning through integration reduces the risk of complications during and after implant placement.
- This includes avoiding damage to nerves, ensuring optimal bone support, and minimizing the potential for post-operative issues.
- Enhanced Predictability:
- The integration of radiographic guides and templates enhances the predictability of implant procedures.
- Practitioners can foresee challenges, plan for variations in anatomy, and implement strategies for a smoother and more predictable outcome.
From comprehensive imaging to meticulous planning and accurate placement, this integration enhances the overall success and predictability of implant procedures, contributing to optimal patient outcomes.
Addressing Challenges Through X-Ray Imaging
X-ray imaging stands as a cornerstone in implant dentistry, offering solutions to challenges that practitioners encounter. This section delves into two significant areas where X-rays play a crucial role: addressing bone deficiencies through grafting procedures and navigating anatomical complexities for successful implant placement.

Bone Deficiency Solutions: The Role of X-Ray Precision
- Identifying Bone Deficiencies:
- X-rays provide a detailed view of the patient’s jawbone, aiding in the identification of areas with insufficient bone density.
- This information is pivotal for planning bone grafting procedures to address deficiencies and create a solid foundation for implant placement.
- Planning Grafting Procedures:
- Precise X-ray assessments enable practitioners to plan the type and extent of bone grafting needed.
- Whether autogenous, allograft, or synthetic grafts, X-rays guide practitioners in choosing the most suitable solution based on the patient’s specific bone deficiency.
- Ensuring Graft Success:
- X-rays continue to be instrumental in post-grafting assessments, monitoring the integration of graft material and confirming its success.
- This ongoing evaluation is vital for adapting the treatment plan as needed and ensuring optimal conditions for subsequent implant placement.
Navigating Anatomical Complexities: X-Ray Guidance
- Thorough Assessment of Anatomy:
- X-rays provide a comprehensive view of anatomical structures, helping practitioners navigate complex oral anatomy.
- This includes identifying the position of nerves, sinus cavities, and adjacent teeth, crucial for avoiding complications during implant placement.
- Precision in Implant Planning:
- By understanding the detailed anatomy through X-rays, practitioners can precisely plan implant placement.
- This involves selecting the optimal angle, depth, and position, avoiding anatomical obstacles and ensuring the long-term success of the implant.
- Adapting to Patient-Specific Anatomy:
- Each patient presents a unique oral anatomy, and X-ray guidance allows for personalized treatment plans.
- Practitioners can adapt to variations in bone structure, tooth positioning, and other anatomical nuances, enhancing the predictability of implant procedures.
From identifying and resolving bone deficiencies through grafting procedures to navigating the intricate anatomical landscape for successful implant placement, X-rays contribute to precise planning and optimal outcomes in the journey towards restoring smiles.
Sequential Imaging for Monitoring Treatment Progress
A step-by-step approach is crucial for ensuring the success of the implantation journey. This section illuminates the significance of sequential X-ray imaging in monitoring treatment progress, specifically focusing on tracking the crucial phase of osseointegration and evaluating overall implant success.
A Step-by-Step Approach: How Sequential Imaging Works
- Initial Assessment and Planning:
- The journey begins with the initial X-ray assessment, providing a baseline understanding of the patient’s oral anatomy.
- Practitioners use this information to plan the implant procedure, considering factors such as bone density, anatomical structures, and optimal implant positioning.
- Immediate Post-Implantation Imaging:
- Following implant placement, a post-implantation X-ray is taken to confirm the precise positioning and alignment of the implants.
- This immediate assessment ensures that the implants are in the intended locations and allows for adjustments if needed.
- Tracking Osseointegration:
- Sequential X-ray imaging becomes instrumental in tracking the process of osseointegration.
- Regular X-rays over the subsequent weeks and months reveal the gradual fusion of the implant with the surrounding bone, a critical factor for implant stability.
- Assessing Bone and Tissue Health:
- Beyond osseointegration, sequential imaging aids in assessing the health of surrounding bone and soft tissues.
- Practitioners can identify any signs of complications, ensuring prompt intervention if issues arise.
- Final Evaluation:
- The final stages of treatment involve comprehensive X-ray imaging to evaluate the overall success of the implant.
- Practitioners assess the stability of the implant, the health of surrounding tissues, and confirm the achievement of treatment goals.
Benefits of Sequential Imaging: Ensuring Precision and Success
- Early Detection of Issues:
- Sequential X-ray imaging allows for early detection of any complications or deviations from the treatment plan.
- Timely identification enables practitioners to address issues promptly, minimizing the impact on overall implant success.
- Confirmation of Osseointegration:
- The continuous monitoring of osseointegration through sequential imaging provides confirmation of successful implant integration.
- This reassures both practitioners and patients about the stability and longevity of the implants.
- Adaptive Treatment Strategies:
- If sequential X-rays reveal unexpected developments, practitioners can adapt treatment strategies accordingly.
- This flexibility ensures that the treatment plan remains dynamic and responsive to the unique progress of each patient.
From the initial assessment and planning stages through tracking osseointegration to the final evaluation, this method ensures precision and adaptability, ultimately contributing to the long-term success of dental implant procedures.
Preventing Implant Failure Through Early Detection
Success in implant dentistry hinges on vigilance and proactive measures. This section underscores the pivotal role of X-rays in early detection, emphasizing their contribution to preventing implant failure and ensuring the longevity of dental implants.
Vigilance for Success: The Significance of Early Detection
- Timely Identification of Complications:
- X-rays serve as a vigilant tool for early identification of complications that could lead to implant failure.
- Issues such as infection, improper osseointegration, or structural concerns are detected at their nascent stages, allowing for swift intervention.
- Monitoring Osseointegration:
- The process of osseointegration is closely monitored through X-ray imaging.
- Early signs of insufficient bone integration or complications are promptly recognized, enabling practitioners to take corrective actions and enhance the chances of successful implantation.
- Assessing Implant Stability:
- Regular X-rays are instrumental in assessing the stability of the implanted structure.
- Any signs of instability or misalignment are detected early, preventing potential failure and ensuring the implant serves its function effectively.
- Detecting Peri-Implantitis:
- X-rays play a crucial role in identifying peri-implantitis, an inflammatory condition that can lead to implant failure.
- Early detection allows for targeted treatments, preventing the progression of the condition and preserving the health of the implant.
Contributing to Long-Term Success: The Role of X-Ray Vigilance
- Intervention for Infection Prevention:
- X-rays aid in the early detection of infections around the implant site.
- Timely intervention, such as antibiotic treatment or debridement, helps prevent the spread of infection and ensures the implant’s long-term success.
- Adapting Treatment Plans:
- Early detection through X-rays allows practitioners to adapt treatment plans based on evolving patient conditions.
- This adaptability ensures that the chosen interventions align with the specific needs and progress of each patient, mitigating potential risks of failure.
- Patient Education and Monitoring:
- X-rays contribute to patient education by visually presenting the status of the implant.
- Patients are informed about the importance of regular monitoring and follow-ups, fostering a collaborative approach in ensuring the sustained success of their implants.
From monitoring osseointegration to detecting complications and addressing peri-implantitis, X-ray vigilance contributes to the overall success and longevity of dental implants, providing both practitioners and patients with the assurance of a resilient and enduring dental restoration.
Educating Patients Through X-Ray Visualization
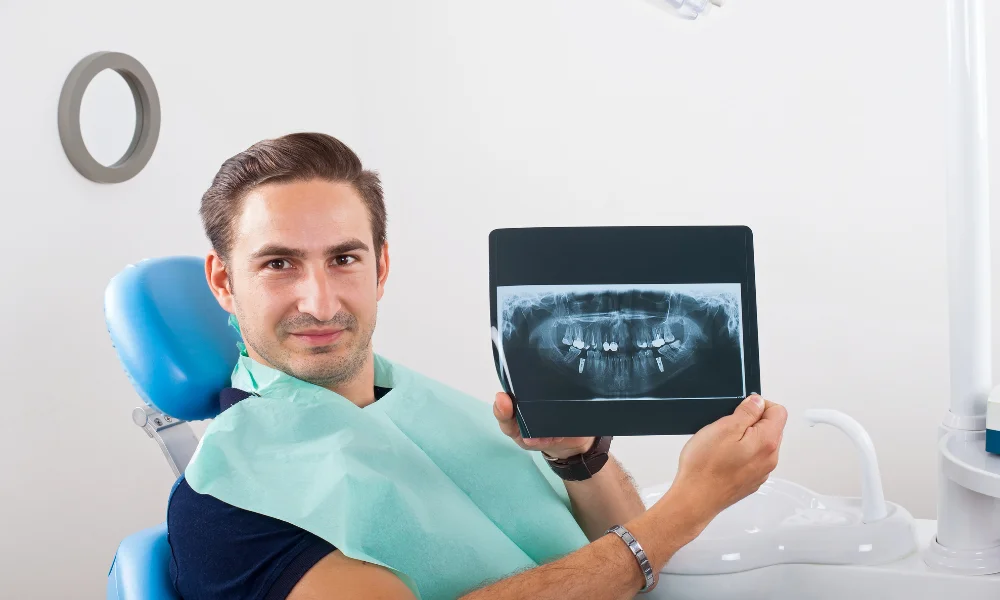
Informed decision-making is paramount in dental treatment. This section explores the valuable role of showcasing X-ray images to patients, elucidating how this visual aid enhances their comprehension of the treatment plan and contributes to fostering informed consent.
Informed Decision-Making: The Power of X-Ray Visualization
- Visualizing Treatment Necessity:
- X-ray images vividly portray the necessity of the proposed treatment plan.
- Patients can visually comprehend issues such as decay, misalignment, or structural concerns, making the need for treatment more tangible.
- Understanding Anatomical Considerations:
- X-rays provide a clear view of the patient’s oral anatomy, allowing for an in-depth understanding of the proposed interventions.
- Patients can grasp how the treatment aligns with their specific anatomical conditions, fostering a sense of personalized care.
- Clarifying Potential Complications:
- Showing X-ray images enables practitioners to transparently discuss potential complications or issues that might arise during or after treatment.
- This transparency empowers patients to make decisions with a comprehensive awareness of possible challenges.
- Highlighting Treatment Progress:
- Sequential X-rays showcase the progress of treatment, visually demonstrating improvements and successful outcomes.
- This dynamic visual narrative reinforces the effectiveness of the chosen interventions, instilling confidence in patients.
Fostering Informed Consent: The Role of X-Ray Visuals
- Transparent Communication:
- X-ray visuals facilitate transparent communication between practitioners and patients.
- Patients appreciate being part of the decision-making process, and X-rays serve as a tangible means to convey information clearly.
- Patient Engagement:
- The visual nature of X-rays engages patients actively in their oral health journey.
- This engagement cultivates a sense of responsibility and collaboration, essential components for successful treatment outcomes.
- Addressing Concerns and Questions:
- X-ray images serve as reference points for addressing patient concerns and questions.
- Practitioners can directly point to visual cues, explaining intricacies and alleviating any uncertainties patients may have.
- Documenting Informed Consent:
- X-ray visuals become part of the documentation of informed consent.
- Patients, having seen and understood the X-rays, provide consent with a more comprehensive understanding of the proposed treatments and potential outcomes.
From understanding treatment necessity to addressing concerns and documenting consent, X-ray visuals contribute to a collaborative and informed partnership between practitioners and patients, ensuring a more engaged and empowered approach to dental care.
Conclusion
From the initial assessment to post-operative monitoring, X-rays stand as invaluable tools, ensuring precision, success, and patient satisfaction. Embracing the technological strides in dental imaging not only enhances treatment planning but also elevates the overall standard of care in the field of dental implantology. For seamless treatment outcomes and patient-centric implant procedures, understanding and harnessing the power of dental implant X-rays is essential. This guide serves as a compass, navigating the intricate landscape of dental implant X-rays for the advancement of modern dentistry.